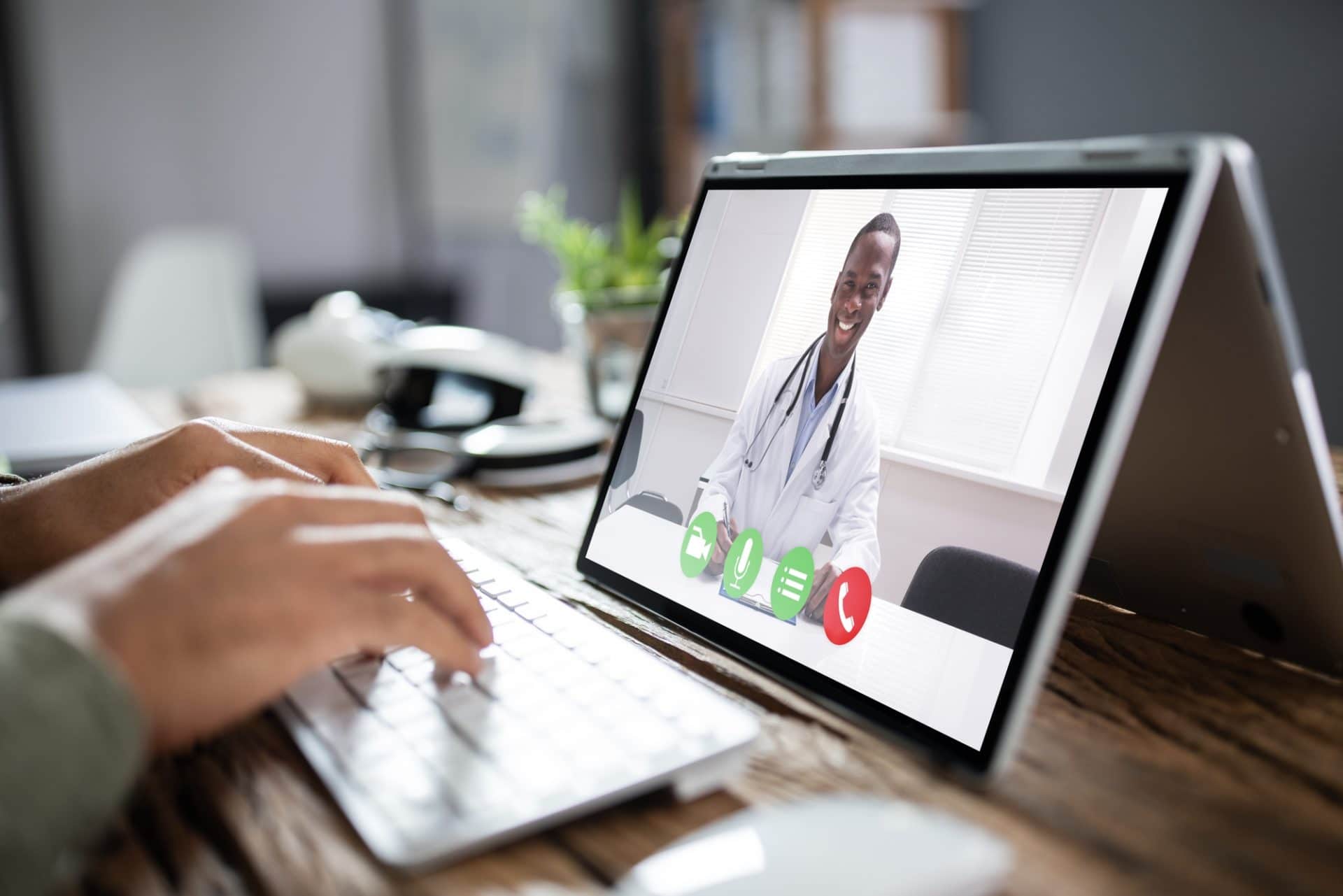
Telemedicine is the practice of medicine using electronic communications, information technology or other electronic means by “a healthcare practitioner for the purpose of facilitating, improving and enhancing clinical, education and scientific healthcare and research”.
The field of Telemedicine has become increasingly popular over the last few decades in line with new developments in technology. Telemedicine is a service that can be used in hospitals, homes, private physician offices and other healthcare facilities.
When referring to the use of Telemedicine, practitioners must adhere to the Ethical Guidelines provided by the Health Professions Council of South Africa (HPCSA) as well as other relevant applicable legislation in South Africa.
It must be noted that normal healthcare services such as “face-to-face” consultations with patients are not being replaced by Telemedicine, it is rather an alternative or complementary tool to the above which helps to enhance access for all South Africans. This includes underserved populations who have limited to no access to healthcare services.
A few HPCSA guidelines to note are for example that the practitioner’s conduct must remain ethical and professional at all times; that confidentiality for the patient must be adhered to at all times; that the consulting practitioner remains responsible for the treatment as well as decisions and other recommendations given to the patient.
In light of the above, the expansion of the use of Telemedicine in South Africa may prove to be very beneficial with its aim to enhance access to healthcare services for all South Africans, as long as the HPSCA’s guidelines are strictly adhered to.
For more information about our e-Health legal service offering to all stakeholders including patients, medical professionals, entrepreneurs and other healthcare organisations contact us here.